There are five substances in the refrigeration system cycle: refrigerants, oil, water, air, and other impurities. The first two are necessary for the normal operation of the system, while the other three substances are harmful to the system but cannot be completely eliminated. At the same time, refrigerants also have three states: vapor, liquid, and gas-liquid mixture. Therefore, once the air conditioning refrigeration system has a malfunction, the symptoms and causes are relatively complex. The following are the eleven common faults of air conditioning refrigeration systems.
1. Fan not turning:
There are two reasons for the fan not turning: one is electrical failure, and the control circuit is not connected; the second is mechanical failure of the fan shaft. When the air conditioning fan in the room does not turn, the room temperature will rise, and the suction and exhaust pressures of the compressor will both decrease to a certain degree. After the air conditioning fan stops turning, the heat exchange efficiency of the room air conditioning coil decreases. When the room cooling load remains unchanged, the room temperature will rise. Due to insufficient heat exchange, the temperature of the refrigerant in the heat exchange coil will decrease relative to the original temperature, that is, the evaporation temperature will decrease, and the cooling coefficient of the system will decrease. The evaporator outlet temperature sensed by the thermal expansion valve also decreases, causing the opening degree of the thermal expansion valve to decrease, and the refrigerant decreases accordingly, so the suction and exhaust pressures also decrease. The overall effect of the decrease in refrigerant flow and cooling coefficient is to reduce the cooling capacity of the system.
2. Low cooling water inlet temperature:
As the cooling water temperature decreases, the discharge pressure, discharge temperature, and filter outlet temperature of the compressor all decrease. However, the room temperature of the air conditioning remains unchanged because the cooling water temperature has not yet decreased to a level that would affect the cooling effect. If the cooling water temperature drops to a certain extent, the condensation pressure will also decrease, causing the pressure difference on both sides of the thermal expansion valve to decrease, and the flow capacity of the thermal expansion valve will also decrease, reducing the amount of refrigerant. Therefore, the cooling effect will decrease.
3. High cooling water inlet temperature:
High cooling water inlet temperature will cause the refrigerant to be too cold, the condensing temperature to be too high, and the condensing pressure to be correspondingly too high. The compression ratio of the compressor increases, the shaft power increases, and the gas transmission coefficient decreases, thus reducing the cooling capacity of the system. Therefore, the overall cooling effect will decrease, and the room temperature of the air conditioning will rise.
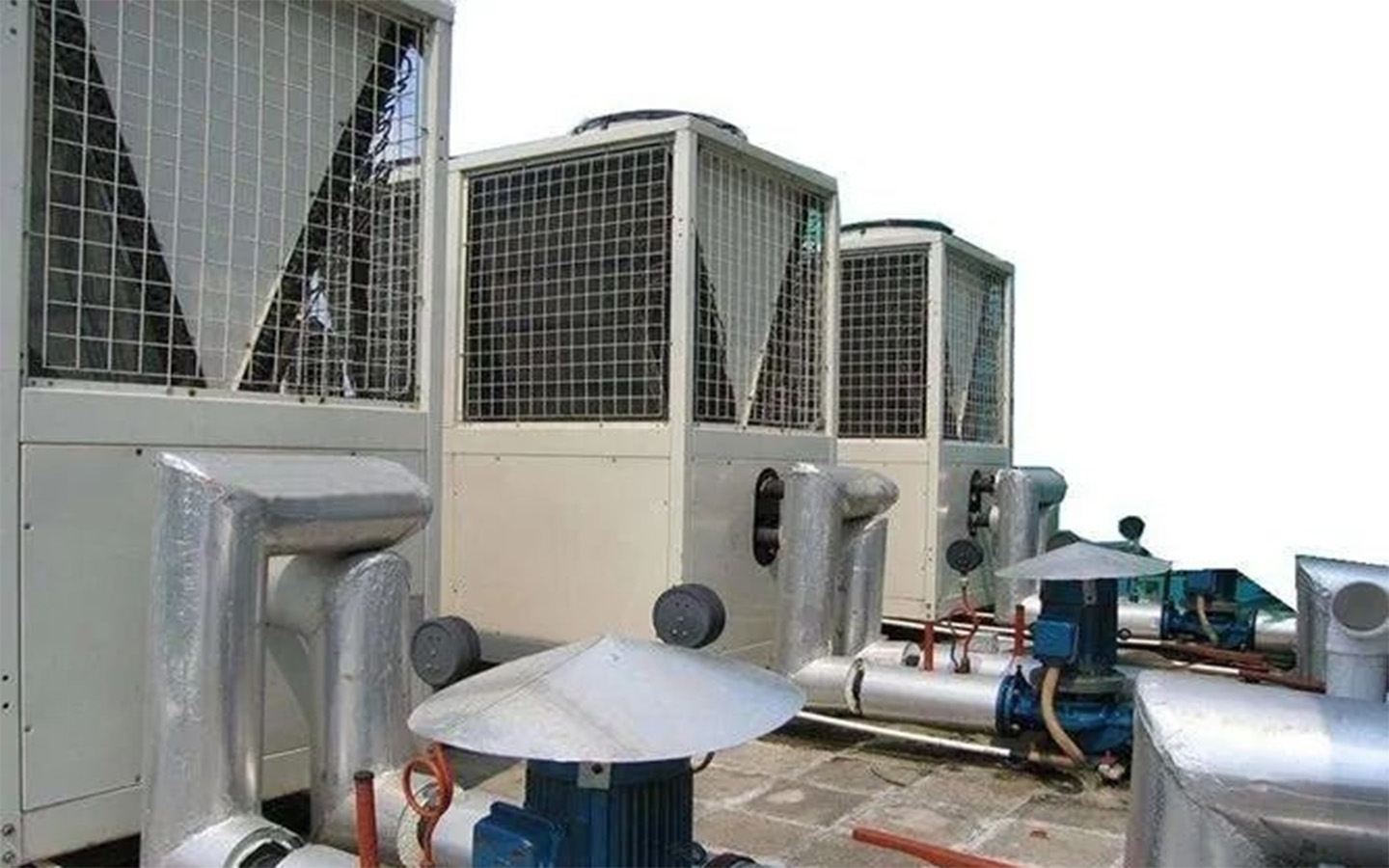

4. The circulating water pump does not turn:
During the debugging and operation of the refrigeration unit, the system circulating water pump should be turned on first. When the circulating water pump does not turn, the outlet temperature of the cooling water and the refrigerant outlet temperature of the condenser increase significantly. Due to the sharp decrease in the cooling effect of the condenser, the suction and discharge temperatures of the compressor also increase rapidly. The rise in condensing temperature also raises the evaporating temperature, but the increase in the evaporating temperature is not as much as the increase in the condensing temperature, so the refrigeration efficiency decreases and the temperature in the air-conditioned room rises rapidly.
5. Filter clogging:
Filter clogging refers to system dirt blockage. Generally, dirt blockage often occurs at the filter because the filter mesh separates the passage section, filtering out debris such as dirt and metal chips. If not cleaned for a long time, refrigeration and air conditioning will be blocked. The consequence of filter clogging is a decrease in the amount of refrigerant circulating in the system. Many of the reasons are similar to the expansion valve opening too small, such as the suction and discharge temperatures of the compressor rising, the suction and discharge pressures of the compressor decreasing, and the air temperature in the air-conditioned room rising. The difference is that the outlet temperature of the filter will become lower. This is because throttling begins at the filter, causing a local temperature drop in the system. When the situation is severe, local frosting or icing may occur in the system.
6. Room load is too large:
Due to the influence of internal and external disturbances and various factors, when the room load of the air conditioner is too large, the temperature in the room will rise, and the two parameters most affected are the suction and discharge temperatures of the compressor. Due to the influence of the heat capacity of the air-conditioned room, it takes some time for other parameters to show obvious changes.
7. Insufficient cooling water flow:
Insufficient cooling water flow and high cooling water inlet temperature are also common faults due to the relationship between the cooling water pipes and valves and the small size of the cooling tower or excessive scaling inside the cooling tower. When the cooling water flow is too low, the heat exchange effect of the condenser decreases, resulting in an increase in the outlet refrigerant temperature of the condenser and an increase in the condensing temperature, which reduces the refrigeration coefficient and affects the refrigeration effect. Under other unchanged conditions, the temperature in the air-conditioned room will also increase to some extent, and the suction temperature of the compressor will also increase. However, the most obvious change is that the temperature difference at the cooling water outlet will become larger and larger.
8. Expansion valve opening is too small:
The expansion valve opening is too small compared to the normal refrigerant charge of the refrigeration system. In this fault, the entire system cycle of the refrigerant is insufficient. When other operating conditions remain unchanged, it cannot fully satisfy the heat absorption of the liquid refrigerant under low pressure gasification. Therefore, the degree of superheat during return air is very large, the suction and discharge temperatures and air temperature in the air-conditioned room will rise, and the suction and discharge pressures will decrease. The outlet refrigerant temperature of the condenser will decrease (i.e., the system’s refrigeration capacity will increase) because the heat exchange capacity of the condenser has not changed, but the circulating refrigerant flow rate in the entire system is very small. Although the refrigeration coefficient increases and the refrigeration capacity per unit refrigeration increases, the total refrigeration capacity decreases, so the temperature in the air-conditioned room will rise.
9. Insufficient refrigerant:
Insufficient refrigerant usually results from two reasons: one is that the amount of refrigerant filled before leaving the factory is insufficient, which generally occurs less frequently; the other is that the refrigerant is insufficient due to valve or welding leaks after the unit has been running for a long time. Therefore, it is a more common fault. The reasons for the fault of insufficient refrigerant and expansion valve opening too small are not significantly different.
10. Excessive refrigerant:
Excessive refrigerant is due to blind refrigerant charge, which is not uncommon in refrigeration system maintenance. This will reduce the effective heat exchange area in the condenser, reduce the heat exchange effect, and cause the condensing temperature to rise and the condensing pressure to increase, resulting in excessive high pressure. When too much refrigerant enters the evaporator and cannot completely vaporize, it is sucked into the compressor, causing high low pressure. The compressor cylinder head will condense or frost, and serious accidents such as liquid impact cylinder may occur. Part of the liquid refrigerant enters the compressor, increasing the motor load, making it difficult to start, and the current overloads during operation. In severe cases, the motor may be burned out due to overload.
11. Compressor damage:
The damage of the compressor scroll plate or suction and discharge valve piece is a common mechanical fault. When the fault occurs, the suction temperature and pressure will increase, and the discharge temperature and pressure will decrease, which is equivalent to reducing the actual gas delivery of the compressor. Therefore, the refrigeration effect is poor, and the temperature in the air-conditioned room will rise rapidly. When the situation is severe, the low-pressure relay will cause the compressor to shut down.

 Español
Español Русский
Русский Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文 suomi
suomi Français
Français Português
Português English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português Pусский
Pусский


