The inverter compressor primarily achieves flow control by changing the motor speed of the compressor through altering the power supply frequency. As refrigeration systems typically operate below their rated load, inverter compressors can function at low frequencies and low cooling capacities to maintain thermal balance with lower power consumption. The refrigerants commonly used in inverter air conditioners include R410A, R32, and a small amount of R290.
Lubricating oil: R22 uses mineral oil (PVE), while R410A employs ester oil (POE). The two oils can only be mixed with their respective refrigerants and cannot be used interchangeably. Ester oil has a tendency to absorb moisture and undergo hydrolysis, necessitating stricter moisture management in the corresponding refrigeration system.
Sealing valves: R22 can use plastic valve cores, whereas R410A can only use steel or copper valve cores. Mixing them is not permissible because the ester lubricating oil used in R410A systems has a swelling effect on plastic valve cores.
Valves include: four-way valves, check valves, and stop valves, among others.
System pressure: R410A systems have higher pressures, typically around 1.6 times that of R22 systems. The requirements for sealing and leak prevention are stricter for R410A refrigerant systems.
Main functions of inverter air conditioner:
1. The compressor frequency automatically adjusts based on the usage conditions.
2. Fast cooling and heating: Automatically determine the room temperature and set temperature when starting up, increase the compressor frequency to achieve rapid temperature rise or drop.
3. Automatically control the operating frequency based on usage conditions. After the room temperature approaches the set temperature, decrease the frequency to maintain stable room temperature and achieve comfort control.
4. High energy efficiency throughout the year, resulting in greater energy savings.
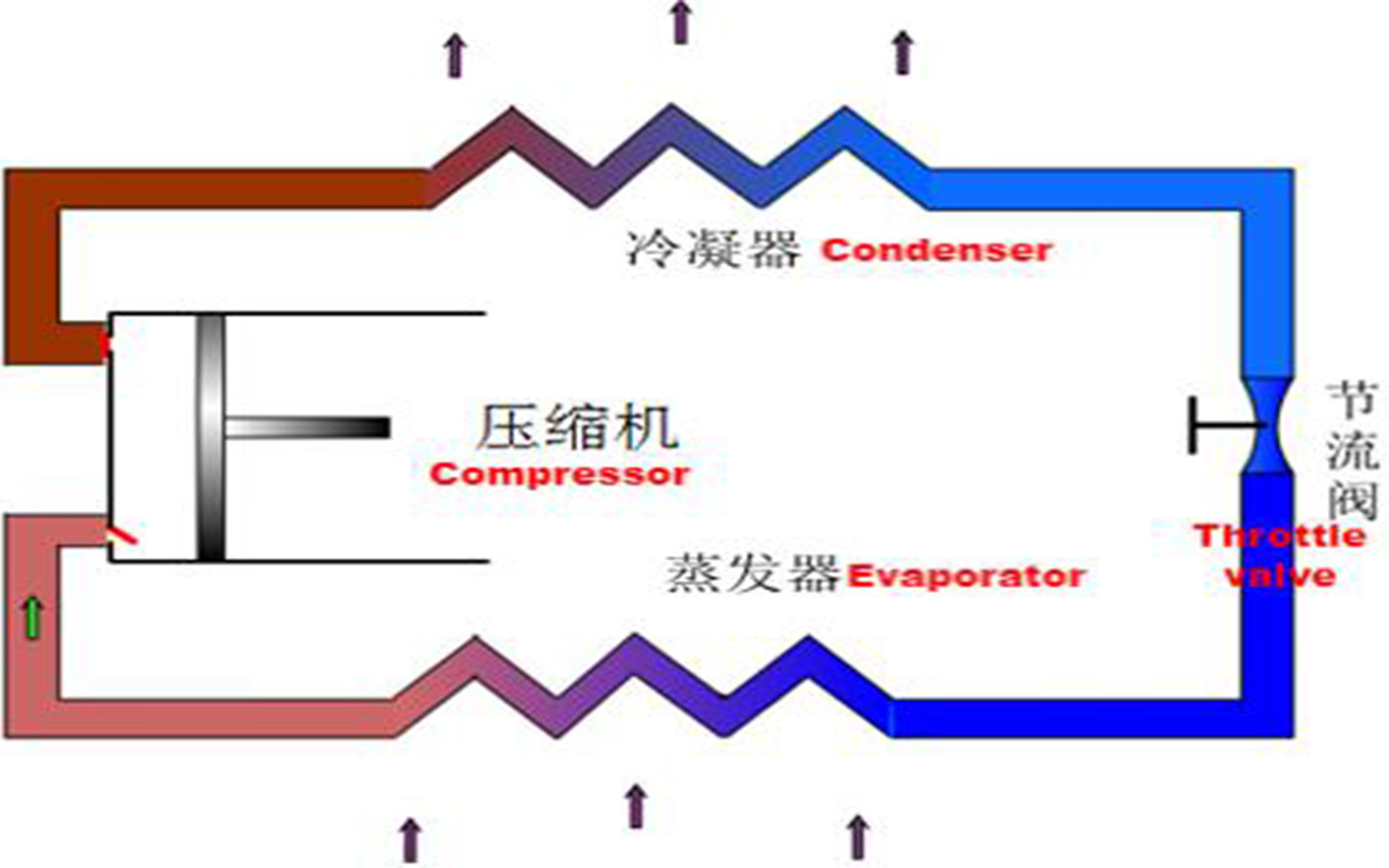
Overview of DC inverter air conditioning system:
The household DC inverter air conditioning system mainly consists of the following components: DC inverter compressor, pressure switch, four-way valve, condenser, throttle device, stop valve, evaporator, outdoor controller, indoor controller, fan, temperature sensor, etc.
Common problems with DC inverter air conditioners:
1. Harm caused by overcharging refrigerant: When excess refrigerant is added to the system, it dilutes the lubricating oil and reduces its viscosity, preventing effective lubrication of the compressor’s roller, cylinder, crankshaft, and slide, leading to increased wear and tear. Additionally, it can cause liquid hammering and fatal damage to the compressor’s pump body. This problem often occurs in multi-split air conditioners.
2. Insufficient refrigerant or refrigerant leakage in the system prevents proper cooling of the electric motor, which leads to increased temperature and can harm its lifespan.
3. Harm caused by dirty heat exchanger surfaces and poor ventilation during installation: Dirt on the surface of the evaporator reduces the refrigerating capacity of the system, putting extra strain on the compressor and decreasing its lifespan. Dirt on the surface of the condenser and poor ventilation during installation increases the system’s load, leading to high temperatures and risking damage to the electric motor’s winding.
4. Harm caused by moisture and non-condensable gases in the system: When the amount of water in the air conditioning system and compressor lubricating oil exceeds the standard, copper plating occurs on the compressor’s components under the high-temperature conditions during operation. Ice blockages can also form at the expansion valve or capillary tube, impairing the compressor’s normal functioning. Non-condensable gases are mainly produced when the refrigeration system is not vacuumed entirely or when there is leakage from the low-pressure side. Failure to purify the entire refrigeration system during installation and maintenance can cause a drop in efficiency and an increase in system pressure.
5. Harm caused by rapid compressor on-off cycles: Due to exceptional circumstances such as low input voltage, refrigerant leakage, or excessive load, the compressor’s overload protection mechanism may repeatedly activate, causing rapid on-off cycles that result in lubricating oil being drawn out of the compressor and not being recirculated, affecting its reliability.
6. Basic structure of electronic expansion valves: Electronic expansion valves consist of a body and coil, with a permanent magnet-type stepping motor as the driving mechanism. The quality of the expansion valve directly determines the system’s operating quality.
l Precautions for using the electronic expansion valve:
– The installation position should be directly above the motor and perpendicular to the center axis of the unit (within ±15 degrees).
– A filter must be installed at the inlet of the valve to prevent foreign objects from entering the valve body.
– The body temperature should not exceed 120 degrees during welding, and the valve body should not be immersed in water when using water cooling.
– The coil area should not have water droplets to prevent reduced lifespan or coil burnout.
– If the valve body falls or experiences strong impact, please check the appearance, current, and flow characteristics, and only use it after confirming it is qualified.
7. Ambient temperature sensor: Used to detect indoor and outdoor ambient temperature, which has a direct relationship with the compressor’s operating frequency. The detected temperature must be accurate.
8. Indoor pipe temperature sensor: Used to detect the temperature of the indoor evaporator. Functions include preventing frost formation during cooling mode and preventing excessive temperature of the indoor evaporator during heating mode.
9. Outdoor pipe temperature sensor: Used to detect the temperature of the outdoor condenser. Functions include preventing excessive temperature of the outdoor condenser during cooling mode and determining if the system is entering or exiting defrost mode during heating mode.
10. Outdoor exhaust sensor: Used to check the temperature at the exhaust pipe outlet. Functions include preventing damage to the compressor coil due to excessive exhaust temperature and participating in the calculation of the electronic expansion valve opening. If the exhaust temperature sensor falls off the exhaust pipe, the system will not function properly, so this must be taken into consideration.
11. High pressure switch: Prevents damage to the system components in the case of abnormal system pressure. The pressure switch will disconnect the system and protect it from operation when the pressure exceeds a certain value. The system can only restart after the pressure returns to normal.
12. Soundproof cotton: The main function of the soundproof cotton on the outdoor unit is to eliminate the noise generated by the compressor. The installation method of the soundproof cotton significantly affects its soundproofing effect. Therefore, after adjusting the soundproof cotton, it must be installed according to the original installation method.
13. Damping block and vibration-absorbing rubber: The vibration-absorbing rubber is used to change the inherent vibration frequency of the pipe. The damping block converts the vibrational energy of the pipe into heat energy to reduce vibration. Therefore, in the maintenance process, the shape, weight, and position of the damping block and vibration-absorbing rubber should be maintained. Any changes may not achieve the desired vibration reduction effect and may even exacerbate the vibration, leading to pipe rupture.

 Español
Español Русский
Русский Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文 suomi
suomi Français
Français Português
Português English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português Pусский
Pусский


