Knowing how to calculate the static and dynamic load of a fan is essential for ensuring efficient and safe operation in industrial applications. ZIBO DECENT MACHINERY CO.,LTD. provides an overview of the parameters and formulas to calculate the static and dynamic load of a fan.
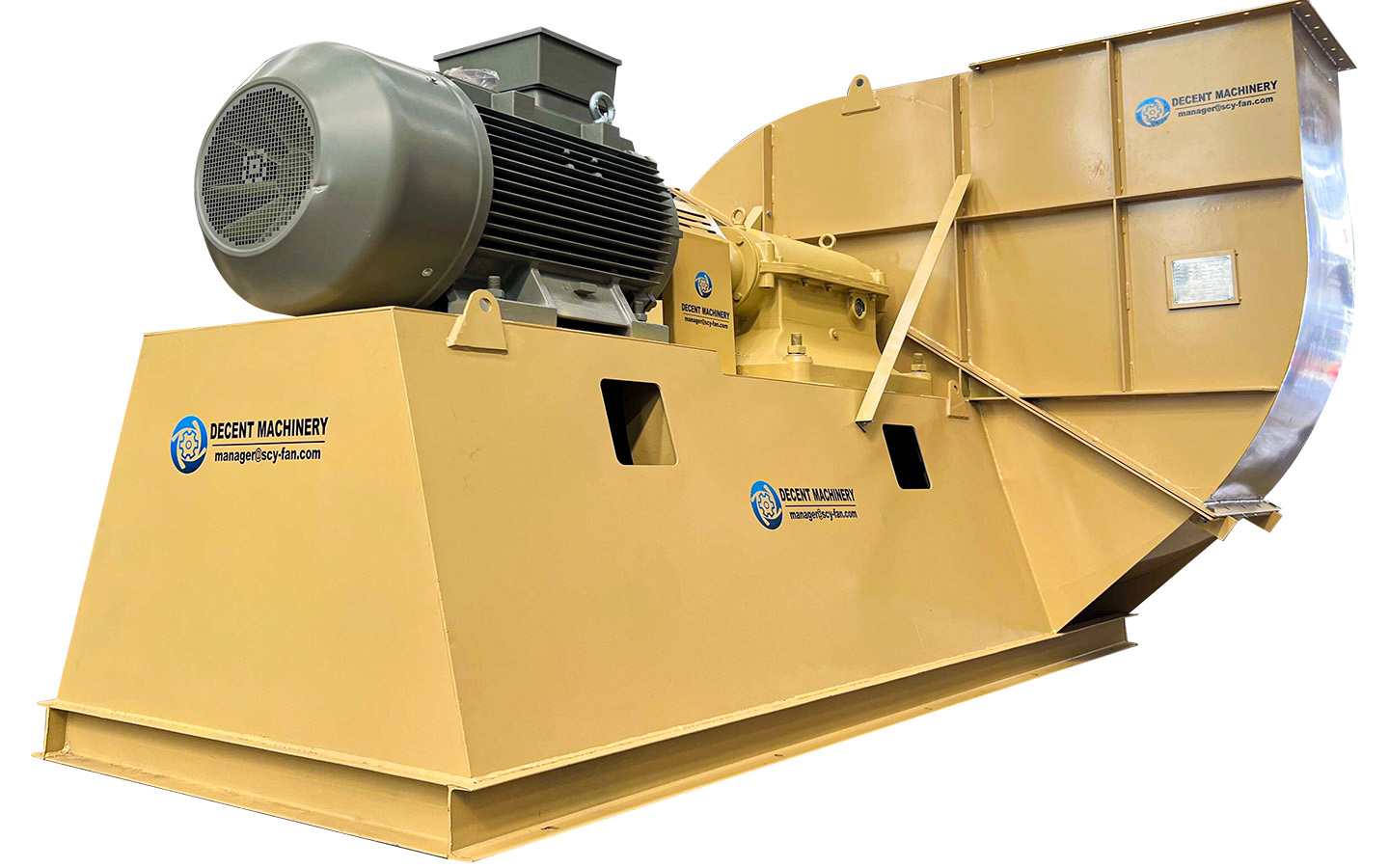

Parameters and Calculation Formula for Static Load:
Flow rate (Q): The amount of gas that a fan processes while working, measured in cubic meters per second (m³/s) or cubic feet per minute (CFM).
Pressure (P): The pressure that a fan generates while working, measured in pascals (Pa) or inches of water column (inH2O).
Fan power (P): The power that a fan draws from a power source, measured in watts (W) or horsepower (hp).
Fan speed (N): The rotational speed of a fan’s impeller, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
Generally speaking, the static load of a fan can be estimated using the following formula: Static Load = Power / N
Parameters and Calculation Formula for Dynamic Load:
Load curve: A curve that shows the variation in fan load under different operating conditions, which is usually provided by the fan manufacturer.
Fan speed (N): The rotational speed of a fan’s impeller, measured in RPM.
The formula for calculating the dynamic load of a fan can be expressed as: Dynamic Load = Load Curve × N
Please note that the parameters and formulas provided here are general concepts. The specific calculation methods and formulas may vary depending on the fan model, operating conditions, and specific requirements. Therefore, it is recommended to consult the technical data provided by the fan manufacturer or seek the advice of a professional engineer to obtain more accurate results.
In conclusion, understanding the parameters and formulas for calculating the static and dynamic load of a fan can be an essential skill for ensuring safe and efficient operation.

 Español
Español Русский
Русский Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文 suomi
suomi Français
Français Português
Português English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português Pусский
Pусский


